Variables
In PHP, variables act like containers that store information you can use throughout your code. They have a name and a value, like a label and the content in a box.
- Naming: Variable names can include letters, numbers, and underscores, but must start with a letter or underscore.
- Data Types: Variables hold different types of data, like text (strings), numbers (integers or floats), or true/false (Booleans).
- Declaration: You declare a variable with a $ symbol followed by its name. You then assign a value using the equal sign (=).
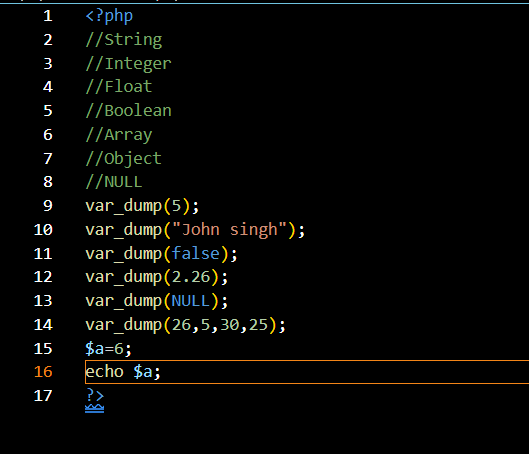
- Example:
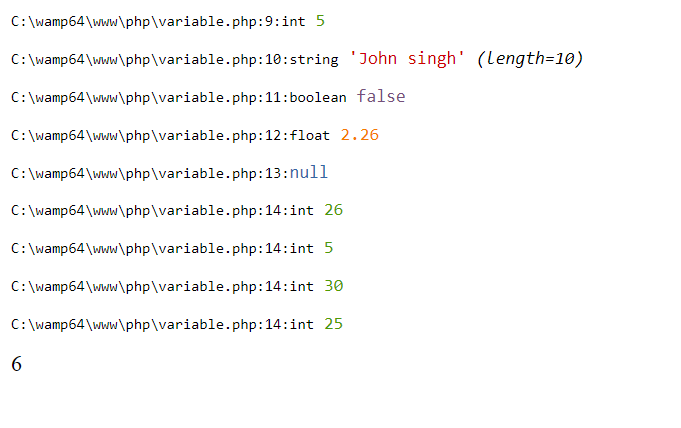
Output
Variables are essential for creating dynamic and interactive web applications with PHP. You can use them to store user input, perform calculations, and control the flow of your program.